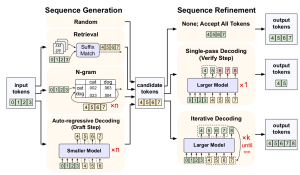
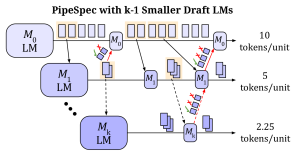
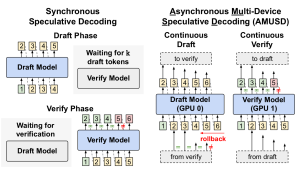
Speculative Decoding
Most existing methods for accelerating large language models (LLMs) focus on compressing or pruning models to reduce the computational cost per token generated. In contrast, speculative decoding takes a fundamentally different approach by attempting to break the sequential dependencies inherent in autoregressive generation. At its core, speculative decoding methods leverage a faster, smaller model (the “draft” model) to rapidly propose candidate tokens, which are subsequently verified by a larger, more accurate “verify” model. This raises at least two compelling research questions:
- How can speculative decoding frameworks best structure draft and verify interactions to maximize parallelism and GPU utilization?
- What algorithmic strategies most effectively balance drafting speed with verification accuracy to ensure overall performance gains?
Early speculative decoding methods typically employed synchronous drafting and verification phases, alternating between candidate generation and parallel verification. Recent advancements have explored continuous and asynchronous speculative decoding techniques, where draft and verify models independently generate and validate tokens in parallel. These approaches substantially improve GPU utilization and decrease latency, leading to significant performance improvements over conventional speculative decoding frameworks.
Less attention has been devoted to systematically designing robust mechanisms for managing speculative execution—particularly strategies for efficiently handling verification failures and rollback scenarios in continuous decoding frameworks.
Relevant Publications
Speculative Decoding and Beyond: An In-Depth Review of Techniques